 Admin
Admin
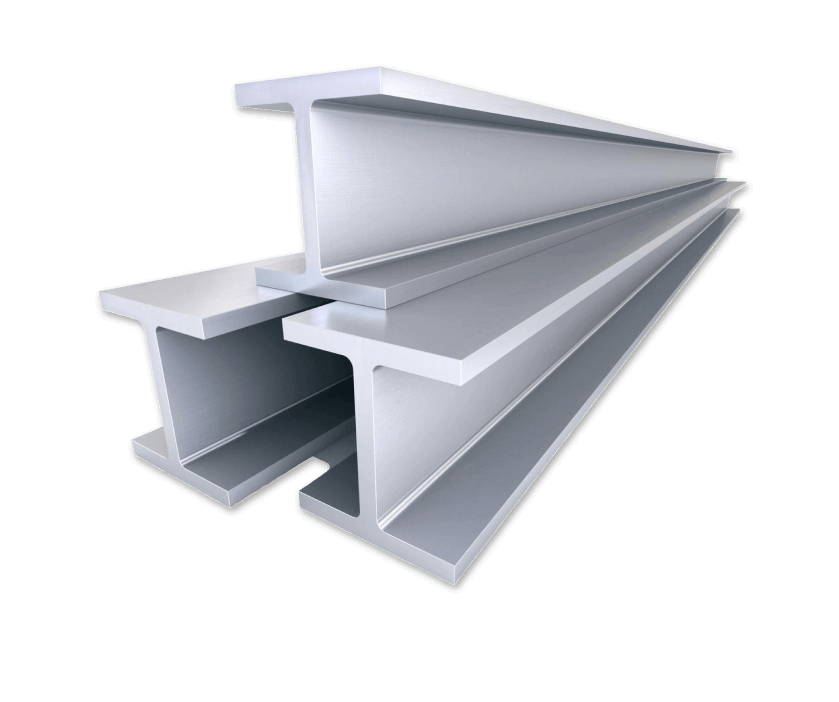
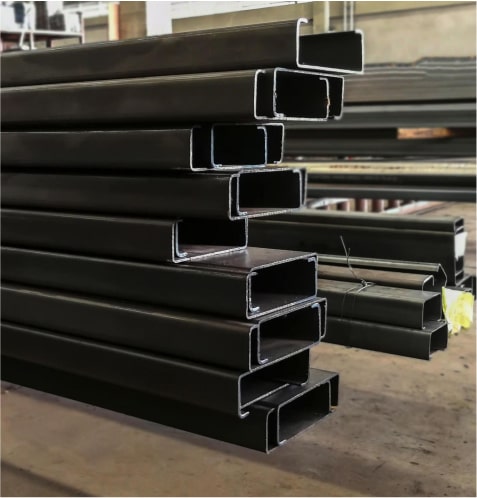
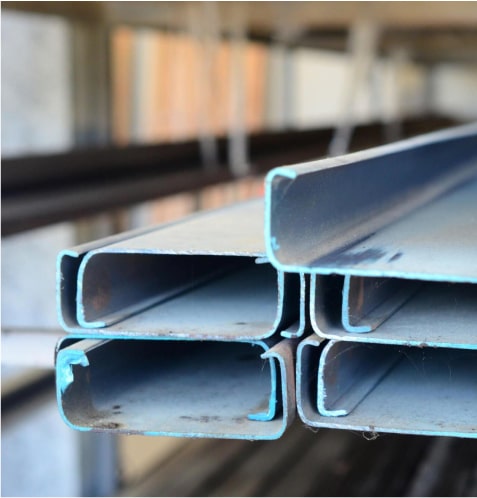
The name is Z-shaped steel because it looks like a “Z,” and it does so for a reason. The structure of it allows for flexibility in structural needs, easy integration with other materials, and excellent strength-to-weight ratios. Whether you’re designing industrial buildings, warehouses, or bridges, Z-shaped steel is a sure bet. What exactly Is Z-shaped steel? Z purlins or Z sections are rolled steel products with a profile resembling the letter “Z.” They are also known as Z-shaped steel. Z purlins are mainly employed to support roofing and cladding systems and are used primarily in structural framework applications. Because of its distinctive design, overlapping connections can improve structural stability and load distribution. Z Shaped Steel Key Features • It is strong and has a lower weight for efficient construction. • Usually treated or coated for use in harsh environments. • Compatible for a wide variety of structural systems. • Reduces the cost of the material without compromising the performance. Load-Bearing Capacity: C-Shaped Steel vs. Z-Beam Let's compare both types of steel to determine which option is best for your project regarding load-bearing capacity. C-Shaped Steel Load-Bearing Capacity: C-shaped steel should be able to handle large vertical loads. The open side of the 'C' is suitable for attaching to other structural parts, making it an excellent choice for first walls, beams, trusses, etc. This makes the closed side of the 'C' extra rigid, providing some protection against deformation under load. C-shaped steel has its limitations. It excels in torsional (twisting) loads but may not perform as adequately in its vertical loads. That is particularly true in applications where the load is off-center and can cause the beam to twist or buckle. Z-Beam Load-Bearing Capacity: However, z-beams have a load distribution designed into them. The Z shape allows a beam to spread its weight evenly throughout its length, reducing the stress on any one point. Z-beams are particularly effective in applications where the load is spread out, e.g., roofing systems and long-span structures, because this makes them a favorable structural solution. The Z-beam is also compact and can maintain its strength with less material, making it sometimes cheaper. While Z beams are intense for load distribution, they may not be as strong or sturdy as C-shaped steel in resisting heavy vertical loads and torsional forces. Advantages of Z-Shaped Steel in Structural Systems High Load-Bearing Capacity Due to its geometry, z-shaped steel is ideal for supporting roofs, walls, and floors in large structures because of its high load-carrying capacity. Lightweight Construction Being structural steel shapes, Z shapes are lightweight and have lower transportation and installation costs than other shapes. This also makes it easier for them to handle on-site. Flexibility and Versatility A single Z-shaped steel component can construct both simple single-span and intricate multi-span framework arrangements. Its ability to overlap makes Z-shaped steel the perfect material for building seamless structures. Cost-Effective Solution The strength-to-weight ratio enables cost reductions through minimal material utilization while maintaining structural integrity. Resisting Environmental Conditions Z-shaped steel coated or galvanized resists corrosion and is suitable for outdoor and industrial applications where moisture or chemicals are commonplace. Z Shaped Steel Applications Z-shaped steel can be used across industries because of its distinct properties. Below are some of its primary applications: Roofing and Wall Systems Z purlins function as roof and wall claddings and support roofing panels in commercial and industrial buildings, providing stability and lastingness. Bridges and Infrastructure Because of its strength and lightweight nature, it is a prime candidate for bridge components and other infrastructure projects where load-carrying efficiency is imperative. Industrial Building and Warehouse In terms of performance, Z-shaped steel remains a standard structural component used for essential support in warehouses factories and storage facilities. Solar Panel Mounting Systems Z-shaped steel is corrosion-resistant and lightweight, making it suitable for solar panel frames and mounting structures. Why a Z Shaped Steel Is the Perfect Choice for Structural Projects Simplified Construction This overlapping nature of Z-shaped steel results in easy assembly and disassembly during construction, which decreases construction time and lowers labor cost requirements. Enhanced Durability Long-lasting structures can be built with galvanized or treated Z-shaped steel, which offers long-term resistance to environmental stressors. Structural Efficiency Its shape spreads the load over the structure, so it has less chance of failing and will remain stable even under extreme conditions. Adaptable to Custom Designs Engineering and design teams find Z-shaped steel essential because of its adaptable design, which meets various architectural demands. Limitations of Z-Shapes Because of their inherent Z-shapes, these parallel flanges offer excellent structural stability and a good capacity to resist bending and shear forces. Appropriate Z shapes are available in several sizes to accommodate your design and construction flexibility. The shape may constrain its usage in critical torsional or lateral stability applications. To effectively address such limitations, bracing or reinforcing elements may be added. Architectural designs of Z shapes probably involve aesthetic considerations, as the Z form is inconsistent with all aesthetic preferences. While limited in certain respects, Z-shapes have always been integral to structural steel construction due to their strength, stability, and versatility. They have proven capable of bearing their load and adapting to different construction needs. Maintenance Guide: Regular Inspections: Have regular inspections (every six months or annually) for deformation, cracking, corrosion, or looseness. If you have any loose bolts, check and tighten them immediately. Anti-Corrosion Treatment: • layers can be set up or anti-corrosion coatings applied. • During installation of galvanized purlins, protect them from scratching or damaging coating. Proper Use: • Do not overstack or hang excessive weight on purlins to prevent them from being overloaded. • If more loads are needed, redesign the structure and replace purlins when needed. Repair and Replacement: • The damaged components should be repaired or replaced when there is a problem with purlins. • Repair damaged parts and take out the rust. • For replacements, choose materials that match requirements and process them according to design drawings. Enhanced Design and Construction Management: Proper design of purlins during the structure's design phase demands careful consideration of load capacity and stability through appropriate selection of spacing and length and cross-section dimensions. Conclusion Because of its design, durability, strength, and low cost, it is the most preferred material by contractors in different fields. With construction demands in this area shifting, it cannot be overemphasized how crucial it is to select the right materials for enhancing structures. Z-shaped steel fulfills such demands and goes a notch higher to provide more and higher value in all projects.
 Mar 13 2025
Read More
Mar 13 2025
Read More